What is the Database transaction?
A transaction is a single logical unit of work which accesses and possibly modifies the contents of a database. Transactions access data using read and write operations.
All types of database access operation which are held between the beginning and end transaction statements are considered as a single logical transaction. During the transaction the database is inconsistent. Only once the database is committed the state is changed from one consistent state to another.

Example of simple transaction:
START TRANSACTION;
INSERT INTO Users (ID, user_name, email) VALUES
('asdf','bbb','bbb@gmail.com');
INSERT INTO Address (street_address, city, zip_code,permanent, user_id) VALUES
('98 Old Chapel Road','GARWAY','HR2 7XH',1,1),
COMMITIf any part of the above code fails for any reason, unknown column, missing validation value or something. No other query will be performed, transaction ensures that there is no partial completion being recorded in the database.
ACID PROPERTIES are used for maintaining the integrity of database during transaction processing. ACID stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability.
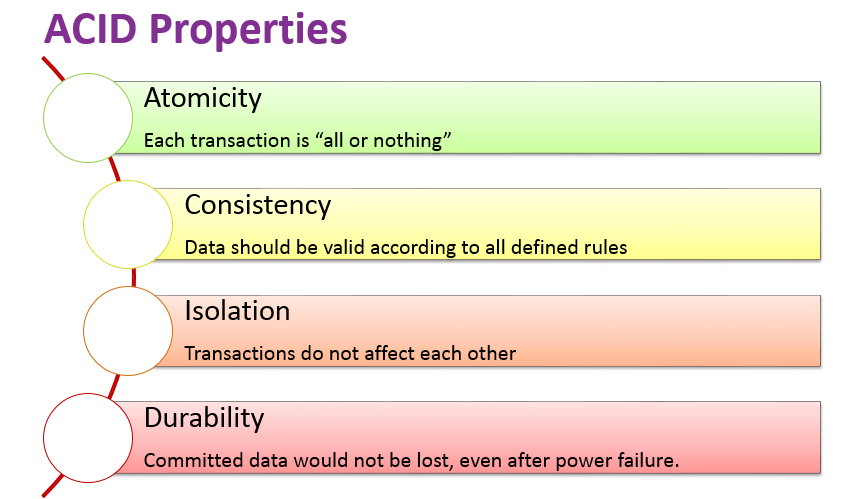
#Atomicity It means that either the entire transaction logic got executed successfully at once or does not happen at all. Transactions do not occur partially. Each transaction runs as one unite. Either to complete the full logic, or nothing executed. It involves the following operations:
- Abort: The changes made to database are not visible
- Commit: The changes made to database are visible.
Atomicity is also known as the ‘All or nothing rule’.
#Consistency Ensures that you guarantee that all data will be consistent. All data will be valid according to all defined rules, including any constraints, cascades, and triggers that have been applied on the database.
Consider the following transaction T consisting of T1 and T2: Transfer of 100 from account X to account Y.
If the transaction fails after completion of T1 but before completion of T2.( say, after write(X) but before write(Y)),
then amount has been deducted from X but not added to Y.
This results in an inconsistent database state. Therefore, the transaction must be executed in entirety in order to ensure correctness of database state.#Isolation Guarantees that multiple transactions can be executed concurrently without causing inconsistency of database state. Transactions occurs independently without interference. The changes occurring with any transaction will not be visible to any any other transaction until it has been committed (Saved).
This property ensures that the execution of transactions concurrently will result in a state that is equivalent to a state achieved these were executed serially in some order.
#Durability Durability means that, once a transaction is committed, it will remain in the system – even if there’s a system crash immediately following the transaction. Any changes from the transaction must be stored permanently. If the system tells the user that the transaction has succeeded, the transaction must have, in fact, succeeded.
The ACID properties of a DBMS allow safe sharing of data. Without these ACID properties, everyday occurrences such using computer systems to buy products would be difficult and the potential for inaccuracy would be huge. Imagine more than one person trying to buy the same size and color of a sweater at the same time -- a regular occurrence. The ACID properties make it possible for the merchant to keep these sweater purchasing transactions from overlapping each other -- saving the merchant from erroneous inventory and account balances.
I think now, We've covered a little more details about ACID, In the next article. I'll try to cover more about states of transactions. 🔥
Peace ✌️